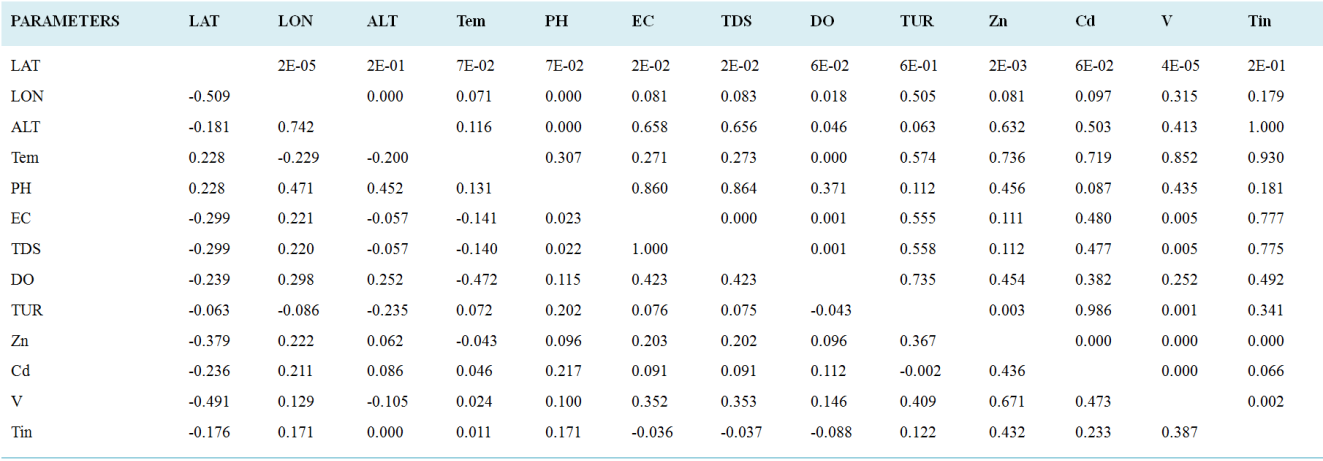
This study investigates the geological and anthropogenic sources of Tin, zinc, cadmium, and vanadium in the western Sokoto Basin, employing multivariate statistical analysis to understand their distribution, interactions, and implications for groundwater quality and environmental management. In Western Sokoto, Nigeria, this research investigates water quality in terms of temperature, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), dissolved oxygen (DO), turbidity (TUR), and concentration of some heavy metals such as zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), vanadium (V), and Tin (Sn). The study employed both in-situ and laboratory analysis. The physical parameters were analysed in situ using hand-held meters. Heavy metals were analysed using an MP-AES machine (Model 4200). The study further applied Principal Component Analysis to analyse the data. Based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) among the parameters, the results showed that EC, TDS, Zn, and V can be described as highly correlated. The combination of these parameters explains 33.042% of the total variance in water quality. In addition, Sn independently accounts for 21.863% of independent information, thus giving a total explanation of 55% overall variability of the dataset. Spatial examination shows different effects of these pollution sources, industrial and agricultural activities, on contamination levels in water quality. The unmitigated concentrations of Cd and Sn's incidences pose high environmental and public health threats. The findings highlight the important role of dissolved ions and heavy metal concentrations on water quality effects that significantly affect regional water resources management. Amongst the significant recommendations are continuous monitoring of water quality to identify pollution hotspots, enforcement of pollution control measures, and targeted remediation in areas with high levels of Cd and Sn. Awareness of water contamination risks and strengthened environmental policies on waste management and water protection are also necessary for sustainable water quality management. The study, therefore, emphasises localized strategies to mitigate contamination and protect water resources concerning the western part of the Sokoto basin.
| Published in | International Journal of Environmental Chemistry (Volume 9, Issue 1) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12 |
| Page(s) | 9-27 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Heavy Metals, Correlation Analysis, Principal Component Analysis, Shallow Groundwater, Sokoto Basin
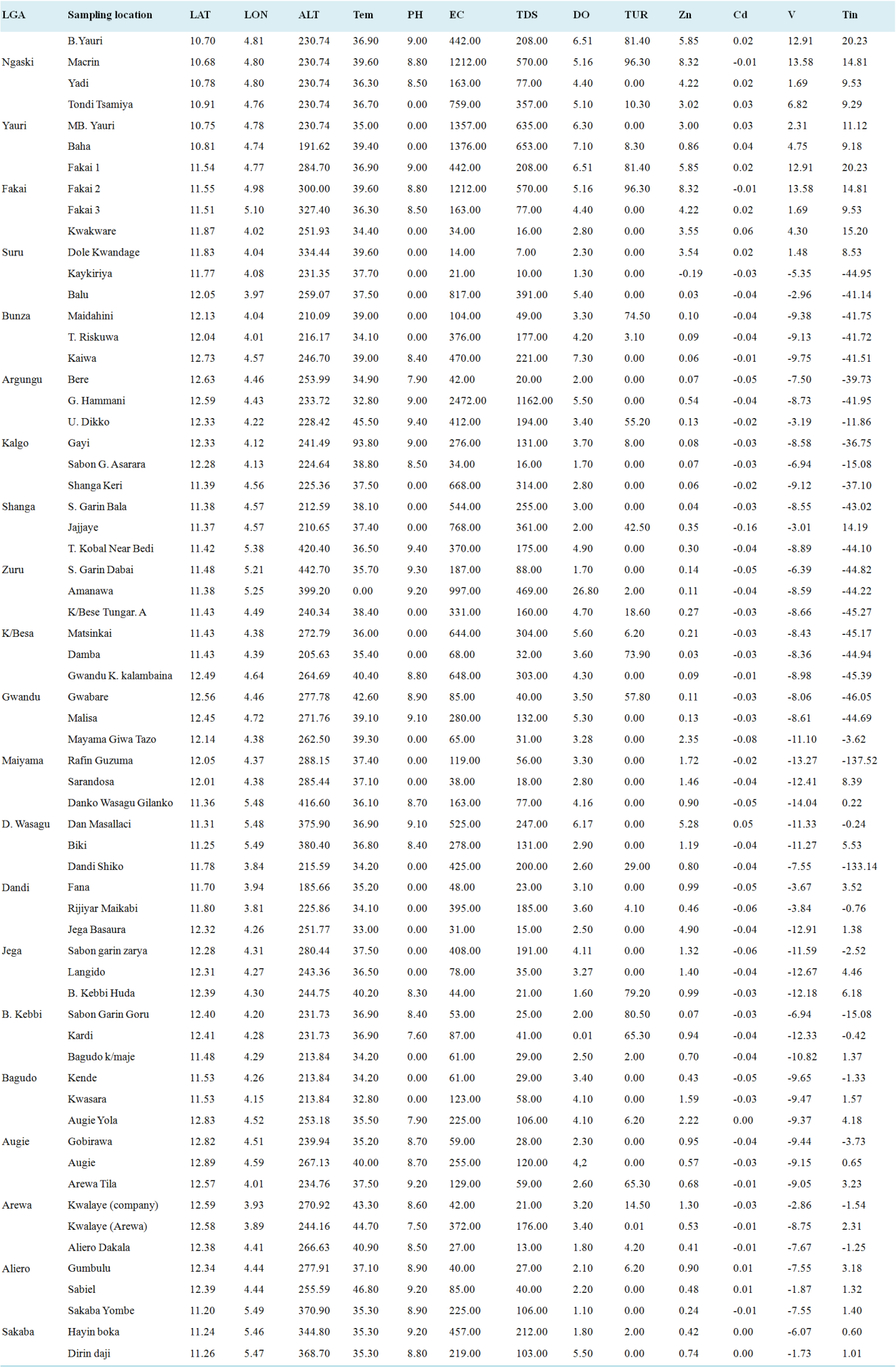
Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | SE | WHO (2011) | NSDWQ (2007) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tem | 30.01 | 93.8 | 38.94 | 0.97 | Ambient | Ambient |
PH | 0 | 9.4 | 4.98 | 0.55 | 6.5-8.5 | 6.5-8.5 |
EC | 14 | 2472 | 390.94 | 54.58 | 500 (uS/cm) | 1000 |
TDS | 7 | 1162 | 184.22 | 25.67 | 1000 | 1000 |
DO | 0.01 | 26.8 | 4.28 | 0.41 | 6.5-8 | |
TUR | 0 | 96.3 | 18.01 | 3.75 | 5 NTU | 5 NTU |
Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | SE | WHO (2011) | NSDWQ (2007) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Zn | -0.19 | 8.32 | 1.517451 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
Cd | -0.16 | 0.06 | 0.02312 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
V | -14.04 | 13.58 | 0.5.53379 | 0 | 0.51 | |
Tin | -137.52 | 20.23 | 0.16.1924 | 0 |
Parameters | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 | PC 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PH | 0.14331 | 0.16151 | 0.44977 | 0.7626 | 0.2104 |
EC | 0.40434 | -0.47068 | -0.09672 | -0.01799 | 0.2007 |
TDS | 0.40429 | -0.47093 | -0.0962 | -0.01869 | 0.19996 |
DO | 0.23932 | -0.34962 | 0.35668 | 0.1439 | -0.22699 |
TUR | 0.23061 | 0.22938 | -0.58136 | 0.51217 | -0.25437 |
Zn | 0.42087 | 0.30403 | -0.11161 | -0.17373 | -0.12649 |
Cd | 0.29939 | 0.24202 | 0.52694 | -0.23814 | -0.40198 |
V | 0.47554 | 0.20775 | -0.13598 | -0.13578 | -0.15011 |
Tin | 0.22174 | 0.40196 | 0.072732 | -0.17151 | 0.74775 |
Eigenvalue | 2.97376 | 1.9678 | 1.04831 | 1.01043 | 0.737654 |
% variance | 33.042 | 21.864 | 11.648 | 11.227 | 8.1962 |
ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
Cd | Cadmium |
DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
EC | Total Dissolved Solids |
LGAs | Local government areas |
LULC | Land use/land cover |
m | Meters |
Max | Maximum |
mg/L | Milligram per Litre |
Min | Minimum |
NSDWQ | Nigerian Standard for Drinking Water Quality |
PC | Principal Component |
PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
pH | Redox Potential |
PO4 | Phosphate |
SE | Standard Error |
Sn | Tin |
TUR | Turbidity |
uS/cm | Micro Siemens per Centimetre |
V | Vanadium |
WHO | World Health Organisation |
Zn | Zinc |
| [1] | Khatri, N. and S. Tyagi, Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Frontiers in life science, 2015. 8(1): p. 23-39. |
| [2] | Akhtar, N., M. I. Syakir Ishak, S. A. Bhawani, and K. Umar, Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water, 2021. 13(19): p. 2660. |
| [3] | Agbasi, J. C., D. A. Ayejoto, J. C. Egbueri, N. Khan, S. I. Abba, V. Ahmad, and M. F. Abuzinadah, HERisk and statistical clustering integrated for health risk modelling of PTEs in natural water resources for drinking and sanitary uses. Toxin Reviews, 2024. 43(4): p. 513-539. |
| [4] | Paul, I. I. and E. N. Bayode, Watershed characteristics and their implication for hydrologic response in the upper Sokoto basin, Nigeria. Journal of Geography and Geology, 2012. 4(2): p. 147-155. |
| [5] | Achugbu, I. C., A. A. Olufayo, I. A. Balogun, J. Dudhia, M. McAllister, E. A. Adefisan, and E. Naabil, Potential effects of land use land cover change on streamflow over the Sokoto Rima River Basin. Heliyon, 2022. 8(7), 1-16 |
| [6] | Obaje, N., M. Aduku, and I. Yusuf, The Sokoto Basin of Northwestern Nigeria: A preliminary assessment of the hydrocarbon prospectivity. Petroleum Technology Development Journal, 2013. 3(2): p. 71-86. |
| [7] | Lamorde, U., U. Umar, T. Ozoji, T. Okonkwo, L. Adamu, and A. Idris-Nda, Advances on the geology and evaluation of potential petroleum systems of the Sokoto basin in NW Nigeria. African Journal of Engineering and Environment Research Vol, 2020. 1(2): p. 78-92. |
| [8] | Ogbesejana, A. B., L. A. Muaz, N. S. Gobirawa, F. D. Radda, S. A. Akinyemi, O. I. Areguamen, O. O. Akintade, A. M. Adeleye, O. M. Bello, and A. C. Egwu, Major, Trace, and Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry of the Late Paleocene Shales from Gamba Formation, Sokoto Basin, Northwest Nigeria. 2024. |
| [9] | Toyin, A. and O. Adekeye, Assessment of chemical and mineralogical composition of tertiary shales from the Nigerian sector of Iullemmeden basin: implication for paleoclimate and provenance. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2019. 150: p. 485-498. |
| [10] | Evrard, C., Y. Fouquet, Y. Moëlo, E. Rinnert, J. Etoubleau, and J. A. Langlade, Tin concentration in hydrothermal sulphides related to ultramafic rocks along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: a mineralogical study. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2015. 27(5): p. 627-638. |
| [11] | Marahrens, J., Tin isotope analysis of tin ore deposits in Europe and Central Asia in view of the tin provenance in archaeological metal objects. 2023. |
| [12] | Wu, T., R. Yang, L. Gao, J. Li, and J. Gao, Origin and enrichment of vanadium in the lower Cambrian black shales, south China. ACS Omega, 2021. 6(41): p. 26870-26879. |
| [13] | Michie, M., Vanadium Isotopic Analysis of Extractable Organic Matter and Bulk Rock Shale in the Eagle Ford Shale. 2019, University of Houston. |
| [14] | Awogbami, S. O., Assessment of Water Quality and Its Associated Health Effects Among Residents of Gold Mining Areas in Osun State, Southwest Nigeria. 2023, Kwara State University (Nigeria). |
| [15] | Dharma-Wardana, M., Fertilizer usage and cadmium in soils, crops and food. Environmental geochemistry and health, 2018. 40(6): p. 2739-2759. |
| [16] | Nacke, H., A. Gonçalves, D. Schwantes, I. Nava, L. Strey, and G. Coelho, Availability of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, and Cr) in agriculture from commercial fertilizers. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2013. 64: p. 537-544. |
| [17] | Sarkingobir, Y., U. Tambari, A. Imam, M. Abubakar, M. Sahabi, and S. Aliyu, Solid waste disposal and extent of selected heavy metals in Fadama area of Sokoto city, Nigeria. Journal of Bioresources and Environmental Sciences, 2023. 2(3): p. 39-49. |
| [18] | Offor, I. F., G. U. Adie, and G. R. Ana, Review of particulate matter and elemental composition of aerosols at selected locations in Nigeria from 1985–2015. Journal of Health and Pollution, 2016. 6(10): p. 1-18. |
| [19] | Vareda, J. P., A. J. Valente, and L. Durães, Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019. 246: p. 101-118. |
| [20] | Nouri, J., A. Mahvi, G., Jahed, and A. Babaei, Regional distribution pattern of groundwater heavy metals resulting from agricultural activities. Environmental geology, 2008. 55: p. 1337-1343. |
| [21] | Plum, L. M., L. Rink, and H. Haase, The essential toxin: impact of zinc on human health. International journal of environmental research and public health, 2010. 7(4): p. 1342-1365. |
| [22] | Mansor, M. i., M. O. Fatehah, H. A. Aziz, and L. K. Wang, Occurrence, Behaviour and Transport of Heavy Metals from Industries in River Catchments, in Industrial Waste Engineering. 2024, Springer. p. 205-277. |
| [23] | Korkanç, S. Y., M. Korkanç, and A. F. Amiri, Effects of land use/cover change on heavy metal distribution of soils in wetlands and ecological risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 2024. 923: p. 171603. |
| [24] | Gaaloul, N., S. Eslamian, and B. Laignel, Contamination of groundwater in arid and semi-arid lands, in Handbook of drought and water scarcity. 2017, CRC Press. p. 291-314. |
| [25] | Abu Salem, H. S., M. Albadr, M. M. El Kammar, M. M. Yehia, and A. M. El-Kammar, Unraveling the hydrogeochemical evolution and pollution sources of shallow aquifer using multivariate statistical analysis and hydrogeochemical techniques: a case study of the Quaternary aquifer in Beni Suef area, Egypt. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2023. 195(6): p. 670. |
| [26] | Srivastava, P. K., D. Han, M. Gupta, and S. Mukherjee, Integrated framework for monitoring groundwater pollution using a geographical information system and multivariate analysis. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2012. 57(7): p. 1453-1472. |
| [27] | Wali, S., M. Gada, and I. Dankani, Relating groundwater to geology in Sokoto basin, northwestern Nigeria using multivariate and regression analysis: implications for groundwater availability. Int J Hydro, 2022. 6(2): p. 57-65. |
| [28] | Arogundade, A. B., O. D. Ajama, I. S. Ayinde, S. C. Falade, and M. O. Awoyemi, Investigation of structural controls on the drainage system of northwestern Nigeria. Acta Geophysica, 2023. 71(4): p. 1747-1762. |
| [29] | Wali, S. U., N. Alias, and S. B. Harun, Hydrogeochemical evaluation and mechanisms controlling groundwater in different geologic environments, Western Sokoto Basin, Northwestern Nigeria. SN Applied Sciences, 2020. 2(1808): p. 1-28. |
| [30] | Wali, S. U., N. B. Alias, and S. B. Harun. Understanding Variability of Groundwater Potentials in Western Sokoto Basin: Implications for Sustainable Groundwater Development. in Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Water Resources (ICWR) – Volume 2. 2023. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. |
| [31] | Labbo, A. and F. Ugodulunwa, An interpretation of total intensity aeromagnetic maps of part of southeastern Sokoto basin. Journal of engineering and applied sciences, 2007. 3: p. 15-20. |
| [32] | Toyin, A., O. Adekeye, R. Bale, Z. Sanni, and O. Jimoh, Lithostratigraphic description, sedimentological characteristics and depositional environments of rocks penetrated by Illela borehole, Sokoto Basin, NW Nigeria: A connection between Gulf of Guinea Basins. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016. 121: p. 255-266. |
| [33] | Nwankwo, L. I. and A. T. Shehu, Evaluation of Curie-point depths, geothermal gradients and near-surface heat flow from high-resolution aeromagnetic (HRAM) data of the entire Sokoto Basin, Nigeria. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2015. 305: p. 45-55. |
| [34] | Ola-Buraimo, A., R. Oladimeji, and A. Faruk, Palynology, Paleoenvironment and Stratigraphy Relationship of Tungan Buzu Hill With Adjacent Valley Gwandu Formation, Sokoto Basin, Northwestern Nigeria. Palynology, 2022. 5(2): p. 15-26. |
| [35] | Anderson, H. R. and W. Ogilbee, Aquifers in the Sokoto Basin, Northwestern Nigeria, With a Description of the General Hydrogeology of the Region: Contributions to the Hydrology of Africa and the Mediterranean Region. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1757-L, 1973: p. 1-88. |
| [36] | Oteze, G., Water resources in Nigeria. Environmental geology, 1981. 3(4): p. 177-184. |
| [37] | Wali, S. U., M. A. Gada, I. M. Dankani, and I. Hamisu, Relating groundwater to geology in Sokoto basin, northwestern Nigeria using multivariate and regression analysis: implications for groundwater availability. International Journal of Hydrology, 2022. 6(2): p. 57-65. |
| [38] | Wali, S. U., I. Hamisu, K. J. Umar, M. A. Gada, and I. G. Abor, Evaluation of shallow groundwater in Rural Kebbi State, NW Nigeria, using multivariate analysis: implication for groundwater quality management. MOJ Ecology & Environmental Sciences, 2022. 7(3): p. 65-75. |
| [39] | Yakubu, M. and A. Ojanuga, Characteristics and classification of soils on quaternary coversand in Sokoto-Rima Basin. Agro-Science, 2012. 11(1): p. 21-32. |
| [40] | Auduson, A. and K. Onuoha, Cretaceous Bida and Sokoto Basins of Nigeria: Deducing Basin Architecture and Basement Topography from Aeromagnetic Data Analyses. Int J Earth Sci Geophys, 2020. 6: p. 043. |
| [41] | Wali, S., S. Abubakar, I. Dankani, M. Gada, and A. Usman, Hydrogeology and hydrochemistry of the Sokoto basin, Northwestern Nigeria: A review. Sokoto J Geogr Environ, 2019. 1(1): p. 106-22. |
| [42] | Wali, S. U., N. Alias, S. B. Harun, K. J. Umar, M. A. Gada, I. M. Dankani, I. U. Kaoje, and A. A. Usman, Water quality indices and multivariate statistical analysis of urban groundwater in semi-arid Sokoto Basin, Northwestern Nigeria. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2022. 18(100779): p. 1-18. |
| [43] | Shankar, B., A. Halls, and J. Barr, The effects of surface water abstraction for rice irrigation on floodplain fish production in Bangladesh. International journal of water, 2005. 3(1): p. 61-83. |
| [44] |
O'Neill, A., Nigeria: Urbanization from 2010 to 2020. Statista, 2021.
https://www.statista.com/statistics/455904/urbanization-in-nigeria/ p. 1-2. |
| [45] | Odey, M. O., O. R. Ibor, A. B. Andem, I. Ettah, and A. V. Chukwuka, Drinking water quality and risk implications for community health: A case study of shallow water wells and boreholes in three major communities in Northern Cross-River, Southern Nigeria. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 2018. 24(2): p. 427-444. |
| [46] | Cherian, A. G., Z. Liu, M. J. McKie, H. Almuhtaram, and R. C. Andrews, Microplastic removal from drinking water using point-of-use devices. Polymers, 2023. 15(6): p. 1331. |
| [47] | Marghade, D., D. B. Malpe, and A. B. Zade, Geochemical characterization of groundwater from northeastern part of Nagpur urban, Central India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011. 62(7): p. 1419-1430. |
| [48] | Trick, J. K., M. Stuart, and S. Reeder, Contaminated groundwater sampling and quality control of water analyses, in Environmental geochemistry. 2008, Elsevier. p. 29-57. |
| [49] | García-Ávila, F., L. Ramos-Fernández, D. Pauta, and D. Quezada, Evaluation of water quality and stability in the drinking water distribution network in the Azogues city, Ecuador. Data, in brief, 2018. 18: p. 111-123. |
| [50] | Srihari, S., T. Subramani, V. Prapanchan, and P. Li, Human health risk perspective study on characterization, quantification and spatial distribution of microplastics in surface water, groundwater and coastal sediments of thickly populated Chennai coast of South India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess, 2023. 29: p. 222-244. |
| [51] | Dean, J. R., Methods for environmental trace analysis. Vol. 12. 2003: John Wiley and Sons. |
| [52] | Khan, S. R., B. Sharma, P. A. Chawla, and R. Bhatia, Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES): a powerful analytical technique for elemental analysis. Food Analytical Methods, 2022: p. 1-23. |
| [53] | Okorie, C. N., M. D. Thomas, R. M. Méndez, E. C. Di Giuseppe, N. S. Roberts, and L. Márquez-Magaña, Geospatial Distributions of Lead Levels Found in Human Hair and Preterm Birth in San Francisco Neighborhoods. International journal of environmental research and public health, 2021. 19(1): p. 86. |
| [54] | Wei, H., H. Yu, G. Zhang, H. Pan, C. Lv, and F. Meng, Revealing the correlations between heavy metals and water quality, with insight into the potential factors and variations through canonical correlation analysis in an upstream tributary. Ecological Indicators, 2018. 90: p. 485-493. |
| [55] | Bartoli, G., S. Papa, E. Sagnella, and A. Fioretto, Heavy metal content in sediments along the Calore river: relationships with physical-chemical characteristics. Journal of Environmental Management, 2012. 95: p. S9-S14. |
| [56] | Liu, J., H. Kang, W. Tao, H. Li, D. He, L. Ma, H. Tang, S. Wu, K. Yang, and X. Li, A spatial distribution–Principal component analysis (SD-PCA) model to assess pollution of heavy metals in soil. Science of The Total Environment, 2023. 859: p. 160112. |
| [57] | Chung, S., S. Venkatramanan, N. Park, T. Ramkumar, S. Sujitha, and M. Jonathan, Evaluation of physico-chemical parameters in water and total heavy metals in sediments at Nakdong River Basin, Korea. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016. 75: p. 1-12. |
| [58] | Wali, S. U., N. B. Alias, S. Bin Harun, K. J. Umar, I. G. Abor, A. Abba, and A. Buba, Application of principal component analysis in the context of multivariate statistics and its use for hydrogeochemical analysis. Environmental Engineering & Management Journal (EEMJ), 2023. 22(2). |
| [59] | Nazzal, Y., F. K. Zaidi, I. Ahmed, H. Ghrefat, M. Naeem, N. S. Al-Arifi, S. A. Al-Shaltoni, and K. M. Al-Kahtany, The combination of principal component analysis and geostatistics as a technique in assessment of groundwater hydrochemistry in arid environment. Current Science, 2015: p. 1138-1145. |
| [60] | Kokot, S., M. Grigg, H. Panayiotou, and T. Phuong, Data Interpretation by some Common Chemometrics Methods. Electroanalysis, 1998. 10(16): p. 1081-1088. |
| [61] | Machiwal, D. and M. K. Jha, Identifying sources of groundwater contamination in a hard-rock aquifer system using multivariate statistical analyses and GIS-based geostatistical modeling techniques. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 2015. 4: p. 80-110. |
| [62] | Kumar, A. and A. Singh, Pollution source characterization and evaluation of groundwater quality utilizing an integrated approach of Water Quality Index, GIS, and multivariate statistical analysis. Water Supply, 2024. 24(10): p. 3517-3539. |
| [63] | Alam, A. and A. Singh, Groundwater quality assessment using SPSS based on multivariate statistics and water quality index of Gaya, Bihar (India). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2023. 195(6): p. 687. |
| [64] | Wang, H.-Y., H.-M. Guo, W. Xiu, J. Bauer, G.-X. Sun, X.-H. Tang, and S. Norra, Indications that weathering of evaporite minerals affects groundwater salinity and As mobilization in aquifers of the northwestern Hetao Basin, China. Applied Geochemistry, 2019. 109: p. 104416. |
| [65] | Masoud, A. M. and S. A. A. El-Magd, Integration of hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics for identifying groundwater recharge sources of the Eocene carbonate aquifer, Western Desert, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2022. 187: p. 104449. |
| [66] | Rajendiran, T., C. Sabarathinam, B. Panda, and V. Elumalai, Influence of dissolved oxygen, water level and temperature on dissolved organic carbon in coastal groundwater. Hydrology, 2023. 10(4): p. 85. |
| [67] | Datry, T., F. Malard, and J. Gibert, Dynamics of solutes and dissolved oxygen in shallow urban groundwater below a stormwater infiltration basin. Science of the Total Environment, 2004. 329(1-3): p. 215-229. |
| [68] | Younger, P. L. and C. Wolkersdorfer, Mining impacts on the freshwater environment: technical and managerial guidelines for catchment scale management. Mine water and the environment, 2004. 23: p. s2-s80. |
| [69] | Seth, S., Human impacts and management issues in arid and semi-arid regions. International Contributions to Hydrogeology, 2003. 23: p. 289-341. |
| [70] | Boussen, S., A. Sebei, M. Soubrand-Colin, H. Bril, F. Chaabani, and S. Abdeljaouad, Mobilization of lead-zinc rich particles from mine tailings in northern Tunisia by aeolian and runoff processes. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France, 2010. 181(5): p. 459-471. |
| [71] | Liu, Y., T. Gao, Y. Xia, Z. Wang, C. Liu, S. Li, Q. Wu, M. Qi, and Y. Lv, Using Zn isotopes to trace Zn sources and migration pathways in paddy soils around mining area. Environmental Pollution, 2020. 267: p. 115616. |
| [72] | Singh, A. and S. Gupta, Geo-medical problems Vis–a-Vis role of multilevel elemental anomalies through geo-genic sources emergence health disorder: A review. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res., 2015. 6(6): p. 129-152. |
| [73] | Han, G., J. Wang, H. Sun, B. Liu, and Y. Huang, A critical review on the removal and recovery of hazardous Cd from Cd-containing secondary resources in Cu-Pb-Zn smelting processes. Metals, 2022. 12(11): p. 1846. |
| [74] | Batkhishig, B., Iron, Manganese, Chromium, Titanium and Vanadium Deposits. Mineral Resources of Mongolia, 2021: p. 235-263. |
| [75] | Ahn, J. S., S.-J. Youm, and Y.-C. Cho, Geochemical thresholds for vanadium throughout Korea and at potential development sites. 2023. |
| [76] | Lavenir, N. M. J., E. E. M. Junior, and M. Monesperance, Assessment of vanadium in Stream Sediments from River Mbete, Loum Area (Pan-African Fold Belt, Cameroon): Implications for vanadium exploration. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology, 2020. 5(1). |
| [77] | Williams, M., F. Fordyce, A. Paijitprapapon, and P. Charoenchaisri, Arsenic contamination in surface drainage and groundwater in part of the southeast Asian tin belt, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, southern Thailand. Environmental Geology, 1996. 27: p. 16-33. |
| [78] | Ngansom, W., D. Rodphothong, T. Itthipoonthanakorn, S. Niyomdecha, H. Dürrast, W. Intaratat, P. Chanruang, C. Saengkorakot, and M. Yongprawat, Investigation of radiogeology and environmental geochemistry of quarry ponds in post-tin mining areas of Phuket Island, southern Thailand. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024. 451: p. 141934. |
| [79] | Parandoush, K., H. Atapour, and M. A. Riseh, Geochemical signatures of waste rocks around Sarcheshmeh porphyry copper mine dumps, southeastern Iran: Implications for exploration, economic by-products and the environment. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019. 199: p. 31-52. |
| [80] | Palumbo-Roe, B. and R. Dearden, The hyporheic zone composition of a mining-impacted stream: Evidence by multilevel sampling and DGT measurements. Applied geochemistry, 2013. 33: p. 330-345. |
| [81] | Salem, M., R. Souissi, K. Jebali, W. Trabelsi, H. Abderrazak, and F. Souissi, Cadmium recovery from acid leachates of Tunisian phosphoric acid purification residues. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2024: p. 1-14. |
| [82] | Sako, A., J. Yaro, and O. Bamba, Impacts of hydrogeochemical processes and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in the Upper Precambrian sedimentary aquifer of northwestern Burkina Faso. Applied Water Science, 2018. 8(3): p. 1-14. |
| [83] | Pokrovsky, O. and J. Schott, Iron colloids/organic matter associated transport of major and trace elements in small boreal rivers and their estuaries (NW Russia). Chemical Geology, 2002. 190(1-4): p. 141-179. |
| [84] | Shaheen, S. M., D. S. Alessi, F. M. Tack, Y. S. Ok, K.-H. Kim, J. P. Gustafsson, D. L. Sparks, and J. Rinklebe, Redox vanadium chemistry in soils and sediments: Interactions with colloidal materials, mobilization, speciation, and relevant environmental implications-A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2019. 265: p. 1-13. |
| [85] | Huang, J.-H., F. Huang, L. Evans, and S. Glasauer, Vanadium: Global (bio) geochemistry. Chemical Geology, 2015. 417: p. 68-89. |
| [86] | Carlisle, D., Concentration of uranium and vanadium in calcretes and gypcretes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1983. 11(1): p. 185-195. |
| [87] | Purushotham, D., D. Linga, N. Sagar, S. Mishra, G. Naga Vinod, K. Venkatesham, and K. Saikrishna, Groundwater contamination in parts of Nalgonda district, Telangana, India as revealed by trace elemental studies. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2017. 90: p. 447-458. |
| [88] | Shrestha, S., F. Kazama, and T. Nakamura, Use of principal component analysis, factor analysis, and discriminant analysis to evaluate spatial and temporal variations in water quality of the Mekong River. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 2008. 10(1): p. 43-56. |
| [89] | Tripathi, M. and S. K. Singal, Use of principal component analysis for parameter selection for development of a novel water quality index: a case study of river Ganga India. Ecological Indicators, 2019. 96: p. 430-436. |
| [90] | Adjovu, G. E., H. Stephen, and S. Ahmad, A machine learning approach for the estimation of total dissolved solids concentration in lake mead using electrical conductivity and temperature. Water, 2023. 15(13): p. 2439. |
| [91] | Ahmad, T., S. Muhammad, M. Umar, M. U. Azhar, A. Ahmed, A. Ahmad, and R. Ullah, Spatial distribution of physicochemical parameters and drinking and irrigation water quality indices in the Jhelum River. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2024. 46(8): p. 263. |
| [92] | Li, D., Y. Xu, X. Zhang, Z. Yang, S. Wang, Q. He, and Z. Jia, Water quality, natural chemical weathering and ecological risk assessment of the contaminated area of vanadium ore in Yinhua River, China: Evidence from major ions and trace elements. Acta Geochimica, 2022. 41(1): p. 84-99. |
| [93] | Selvam, S., S. Venkatramanan, P. Sivasubramanian, S. Chung, and C. Singaraja, Geochemical characteristics and evaluation of minor and trace elements pollution in groundwater of Tuticorin City, Tamil Nadu, India using geospatial techniques. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2017. 90: p. 62-68. |
| [94] | Hadjipanagiotou, C., A. Christou, A. M. Zissimos, E. Chatzitheodoridis, and S. P. Varnavas, Contamination of stream waters, sediments, and agricultural soil in the surroundings of an abandoned copper mine by potentially toxic elements and associated environmental and potential human health–derived risks: a case study from Agrokipia, Cyprus. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020. 27(33): p. 41279-41298. |
| [95] | Abba, S. I., M. A. Yassin, S. M. H. Shah, J. C. Egbueri, H. E. Elzain, J. C. Agbasi, G. Saini, J. Usaman, N. A. Khan, and I. H. Aljundi, Trace element pollution tracking in the complex multi-aquifer groundwater system of Al-Hassa oasis (Saudi Arabia) using spatial, chemometric and index-based techniques. Environmental Research, 2024. 249: p. 118320. |
| [96] | Ostrakhovitch, E. A., Tin, in Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals. 2022, Elsevier. p. 807-856. |
| [97] | Gillio Meina, E., The influence of water quality characteristics on vanadium toxicity to model aquatic organisms. 2020, University of Saskatchewan. A Thesis to be submitted to the College of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Toxicology Graduate Program University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada, 1-220 |
| [98] | Krupskaya, L., V. Zvereva, and M. Bubnova. Wastes from the processing of tin ore as a potential source of pollution of ecosystems and a reduction in the risk of environmental disasters in the Primorsky Krai. in IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2019. IOP Publishing. |
| [99] | Cheng, X., W. Qi, T. Danek, D. Matysek, Q. Huang, X. Zhao, Z. Zhou, R. Fang, L. Zou, and J. Xu, Heavy metal contamination of surface water and groundwater in and around Gejiu Tin Mine, Southwest China. Inżynieria Mineralna, 2016. 17. |
| [100] | Vincent, J., and A. E. Kirkwood, Variability of water quality, metals and phytoplankton community structure in urban stormwater ponds along a vegetation gradient. Urban Ecosystems, 2014. 17: p. 839-853. |
APA Style
Wali, S. U., Usman, A. A., Aliyu, S., Usman, H. M., Danladi, P. (2025). Geological and Anthropogenic Sources of Tin, Zinc, Cadmium, and Vanadium in Western Sokoto Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Chemistry, 9(1), 9-27. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12
ACS Style
Wali, S. U.; Usman, A. A.; Aliyu, S.; Usman, H. M.; Danladi, P. Geological and Anthropogenic Sources of Tin, Zinc, Cadmium, and Vanadium in Western Sokoto Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Chem. 2025, 9(1), 9-27. doi: 10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12
AMA Style
Wali SU, Usman AA, Aliyu S, Usman HM, Danladi P. Geological and Anthropogenic Sources of Tin, Zinc, Cadmium, and Vanadium in Western Sokoto Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Int J Environ Chem. 2025;9(1):9-27. doi: 10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12
@article{10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12,
author = {Saadu Umar Wali and Abdulqadir Abubakar Usman and Salma Aliyu and Hussaini Muhammad Usman and Peter Danladi},
title = {Geological and Anthropogenic Sources of Tin, Zinc, Cadmium, and Vanadium in Western Sokoto Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis},
journal = {International Journal of Environmental Chemistry},
volume = {9},
number = {1},
pages = {9-27},
doi = {10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ijec.20250901.12},
abstract = {This study investigates the geological and anthropogenic sources of Tin, zinc, cadmium, and vanadium in the western Sokoto Basin, employing multivariate statistical analysis to understand their distribution, interactions, and implications for groundwater quality and environmental management. In Western Sokoto, Nigeria, this research investigates water quality in terms of temperature, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), dissolved oxygen (DO), turbidity (TUR), and concentration of some heavy metals such as zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), vanadium (V), and Tin (Sn). The study employed both in-situ and laboratory analysis. The physical parameters were analysed in situ using hand-held meters. Heavy metals were analysed using an MP-AES machine (Model 4200). The study further applied Principal Component Analysis to analyse the data. Based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) among the parameters, the results showed that EC, TDS, Zn, and V can be described as highly correlated. The combination of these parameters explains 33.042% of the total variance in water quality. In addition, Sn independently accounts for 21.863% of independent information, thus giving a total explanation of 55% overall variability of the dataset. Spatial examination shows different effects of these pollution sources, industrial and agricultural activities, on contamination levels in water quality. The unmitigated concentrations of Cd and Sn's incidences pose high environmental and public health threats. The findings highlight the important role of dissolved ions and heavy metal concentrations on water quality effects that significantly affect regional water resources management. Amongst the significant recommendations are continuous monitoring of water quality to identify pollution hotspots, enforcement of pollution control measures, and targeted remediation in areas with high levels of Cd and Sn. Awareness of water contamination risks and strengthened environmental policies on waste management and water protection are also necessary for sustainable water quality management. The study, therefore, emphasises localized strategies to mitigate contamination and protect water resources concerning the western part of the Sokoto basin.},
year = {2025}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Geological and Anthropogenic Sources of Tin, Zinc, Cadmium, and Vanadium in Western Sokoto Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis AU - Saadu Umar Wali AU - Abdulqadir Abubakar Usman AU - Salma Aliyu AU - Hussaini Muhammad Usman AU - Peter Danladi Y1 - 2025/02/26 PY - 2025 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12 DO - 10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12 T2 - International Journal of Environmental Chemistry JF - International Journal of Environmental Chemistry JO - International Journal of Environmental Chemistry SP - 9 EP - 27 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2640-1460 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijec.20250901.12 AB - This study investigates the geological and anthropogenic sources of Tin, zinc, cadmium, and vanadium in the western Sokoto Basin, employing multivariate statistical analysis to understand their distribution, interactions, and implications for groundwater quality and environmental management. In Western Sokoto, Nigeria, this research investigates water quality in terms of temperature, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), dissolved oxygen (DO), turbidity (TUR), and concentration of some heavy metals such as zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), vanadium (V), and Tin (Sn). The study employed both in-situ and laboratory analysis. The physical parameters were analysed in situ using hand-held meters. Heavy metals were analysed using an MP-AES machine (Model 4200). The study further applied Principal Component Analysis to analyse the data. Based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) among the parameters, the results showed that EC, TDS, Zn, and V can be described as highly correlated. The combination of these parameters explains 33.042% of the total variance in water quality. In addition, Sn independently accounts for 21.863% of independent information, thus giving a total explanation of 55% overall variability of the dataset. Spatial examination shows different effects of these pollution sources, industrial and agricultural activities, on contamination levels in water quality. The unmitigated concentrations of Cd and Sn's incidences pose high environmental and public health threats. The findings highlight the important role of dissolved ions and heavy metal concentrations on water quality effects that significantly affect regional water resources management. Amongst the significant recommendations are continuous monitoring of water quality to identify pollution hotspots, enforcement of pollution control measures, and targeted remediation in areas with high levels of Cd and Sn. Awareness of water contamination risks and strengthened environmental policies on waste management and water protection are also necessary for sustainable water quality management. The study, therefore, emphasises localized strategies to mitigate contamination and protect water resources concerning the western part of the Sokoto basin. VL - 9 IS - 1 ER -